

Knowing the type and grade of the lymphoma helps doctors decide on the best treatment and how soon it should start. Most are slow growing (low grade) but some can be fast growing (high grade). Types of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) So it is not unusual to have more than one biopsy over a number of weeks or months.
CUTANEOUS TCEL LYMPHOMA SKIN
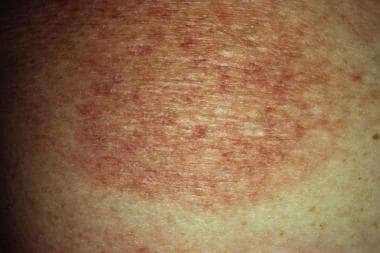
A specialist doctor (pathologist) examines it under a microscope, looking for cancerous T cells.ĭiagnosing skin lymphoma can be difficult. In the early stages, the skin patches can look like other common conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.ĭoctors diagnose CTCL by taking a sample of the affected skin (a biopsy). With darker skin, the patches may appear lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. Many types of CTCL start as flat red patches on the skin, which can sometimes be itchy. For information about cutaneous B cell lymphoma, visit the Lymphoma Action website. The rest of the information on this page is about cutaneous T cell lymphoma. People tend to have lumps on their skin in 1 or 2 areas, rather than affecting all of the body. Several parts of the body can be affected.ĬBCL is a more unusual type. It causes flat red patches on the skin that look like eczema and can be itchy. cutaneous B cell lymphoma (CBCL) starts in the B cells of the skinĬTCL is the most common type of skin lymphoma.cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) starts in the T cells of the skin.In cutaneous lymphoma the T cells or B cells grow out of control within the skin. There are 2 types of lymphocytes or white blood cells:
So they can't fight infection as normal white blood cells do. They start to divide constantly but don't develop fully. When you have lymphoma, some of your lymphocytes don't work properly. The lymph contains a high number of white blood cells (lymphocytes) which fight infection. Tissue fluid called lymph circulates around the body in these vessels and flows through the lymph nodes. The thin tubes are called lymph vessels or lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic system is a network of thin tubes and lymph nodes that run throughout the body. Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. 2003 Jul 149(1):193-6.Skin (cutaneous) lymphoma is a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Bexarotene reverses alopecia in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: an aggressive variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. (2) Gerami P, Rosen S, Kuzel T, Boone SL, Guitart J. The spectrum of hair loss in patients with mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. (1) Bi MY, Curry JL, Christiano AM, Hordinsky MK, Norris DA, Price VH, Duvic M. Combining treatment of cutaneous lymphoma itself along with a specific alopecia therapy may provide the best chance at hair re-growth. Other common treatments for alopecia associated with cutaneous lymphoma include topical or intralesional steroids, Biotin supplementation, topical minoxidil, phototherapy, as well as others. Re-growth, when it occurs, usually begins 3-6 months after the resolution of chemotherapy or radiation. Patients who undergo lower doses of radiation therapy have a higher possibility of new hair growth. In contrast to chemotherapy induced alopecia, hair loss due to radiation is more frequently permanent. Local and total body radiation can also cause hair loss in the areas being treated.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
